 |
|
|
|


|
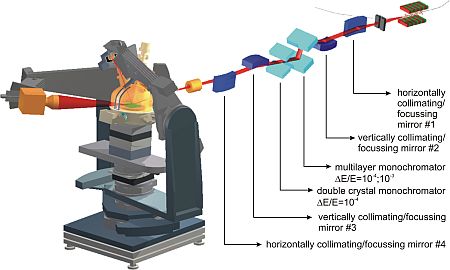
The NANO Beamline at the KIT Light Source is dedicated to high-resolution X-ray diffraction, surface and interface X-ray scattering investigations. The beamline has been optimized to deliver a monochromatic and highly collimated beam with sufficient flux to investigate structural changes and strain evolution during the growth of epitaxial films and superlattices.
In order to carry out real time measurements, different types of environmental chambers, e.g., for molecular beam epitaxy, are mounted on the heavy duty diffractometer which supports up to 500 kg. The diffractometer allows rotation of the sample and the environmental parts in all directions in space. With two different detection systems on the diffractometer, it is possible to perform simultaneous measurement such as Grazing Incidence Small Angle X-ray Scattering (GISAXS), to determine the shape, size, position and correlation in nanostructures, and Grazing Incidence Diffraction (GID) to characterize the surface-patterned structure. One of the main uses of the beamline is to study interface properties like roughness and correlation even for weakly scattering materials such as organic semiconductors.
A further focus of our research is the real time monitoring of nanoparticles and nanostructures. |
|
|
The main scientific applications of the NANO beamine are:
|
|
| name | function | |
|---|---|---|
| Bauer, Sondes | Deputy Head of Department, Beamline Scientist | sondes bauer ∂does-not-exist.kit edu |