In situ Synchrotron X-ray Characterisation of Pulsed Laser Deposition Growth
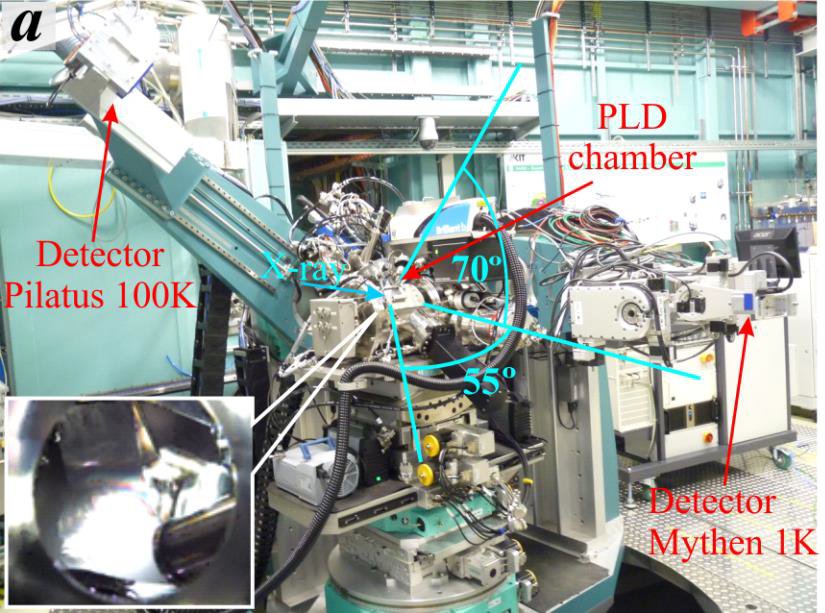
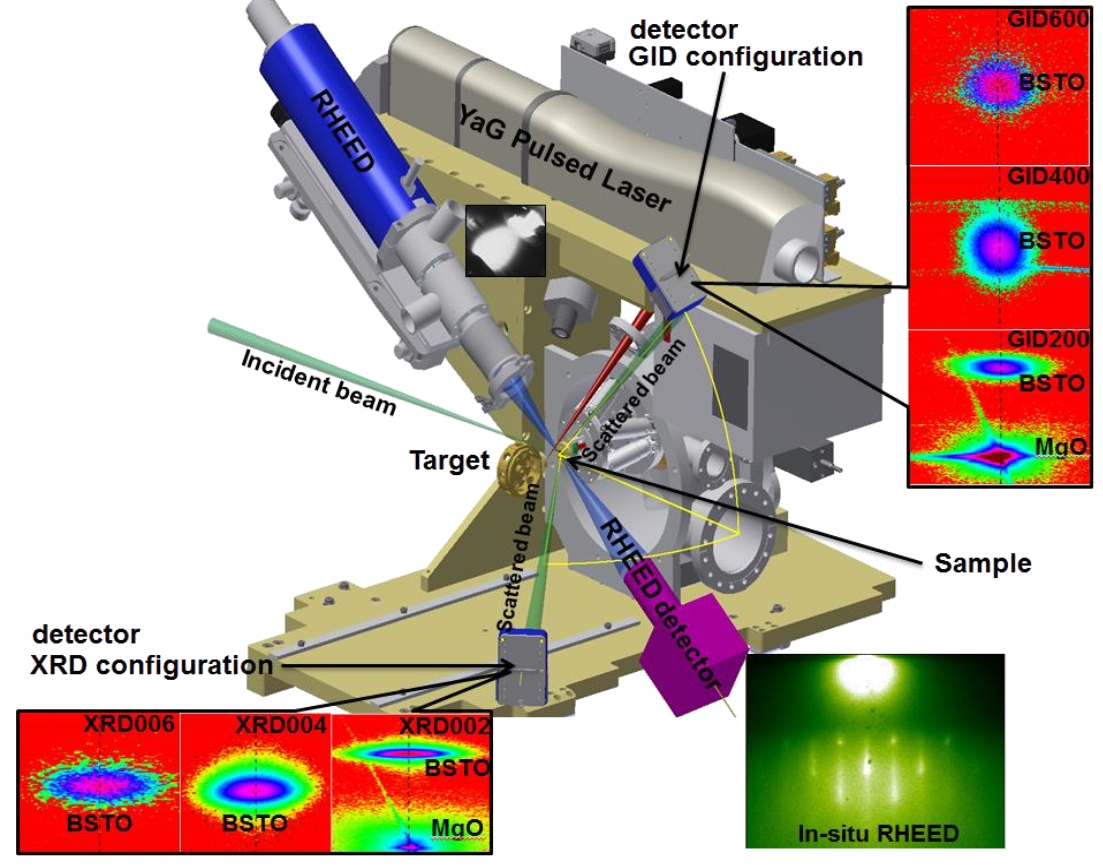
A state-of-the-art pulsed laser deposition (PLD) chamber is installed at the NANO beamline. This instrument is optimised for comprehensive studies on the PLD growth of dielectric, ferroelectric and ferromagnetic thin films in epitaxial oxide heterostructures or even multilayer systems. Combining in situ X-ray reflectivity, in situ two-dimensional reciprocal space mapping of symmetric X-ray diffraction and acquisition of time-resolved diffraction profiles during the deposition process, the PLD chamber offers the opportunity to explore the microstructure of the grown thin films as a function of the substrate temperature, gas pressure, laser fluence and target–substrate separation distance.
|
|
left: PLD chamber mounted on the diffractometer at the NANO beamlne. |
Investigations to date have focused on rare-earth oxides for epitaxial ferroelectric thin films, novel magnetoelectric multiferroics (which exhibit simultaneous ferroelectric & ferromagnetic properties) and substrate materials employed in dielectrics useful for microwave devices.
Related Publications
- Gabriel, V.; Kocán, P.; Bauer, S.; Nergis, B.; Rodrigues, A.; Horák, L.; Jin, X.; Schneider, R.; Baumbach, T.; Holý, V. (2022). Effect of pulse laser frequency on PLD growth of LuFeO3 explained by kinetic simulations of in-situ diffracted intensities. Scientific Reports, 12 (1), Artkl.Nr.:5647. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09414-3
- Bauer, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Horák, L.; Nergis, B.; Jin, X.; Schneider, R.; Gröger, R.; Baumbach, T.; Holý, V. (2021). Time-Resolved Morphology and Kinetic Studies of Pulsed Laser Deposition-Grown Pt Layers on Sapphire at Different Growth Temperatures by in Situ Grazing Incidence Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. Langmuir, 37 (2), 734–749. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02952
- Bauer, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Jin, X.; Schneider, R.; Müller, E.; Gerthsen, D.; Baumbach, T. (2020). Combined In Situ XRD and Ex Situ TEM Studies of Thin Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 Films Grown by PLD on MgO. Crystal research and technology, 55 (9), Art. Nr.: 1900235. doi:10.1002/crat.201900235
- Holý, V.; Bauer, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Horák, L.; Jin, X.; Schneider, R.; Baumbach, T. (2020). In situ grazing-incidence x-ray scattering study of pulsed-laser deposition of Pt layers. Physical review / B, 102 (12), Article: 125435. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.102.125435
- Bauer, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Horák, L.; Jin, X.; Schneider, R.; Baumbach, T.; Holý, V. (2020). Structure Quality of LuFeO3 Epitaxial Layers Grown by Pulsed-Laser Deposition on Sapphire/Pt. Materials, 13 (1), Art. Nr.: 61. doi:10.3390/ma13010061
- Bauer, S.; Rodrigues, A.; Baumbach, T. (2018). Real time in situ x-ray diffraction study of the crystalline structure modification of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 during the post-annealing. Scientific reports, 8 (1), Article No. 11969. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-30392-y
- Rodrigues, A.; Bauer, S.; Baumbach, T. (2018). Effect of post-annealing on the chemical state and crystalline structure of PLD Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 films analyzed by combined synchrotron X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Ceramics international, 44 (13), 16017–16024. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.038